Genome-wide reconstruction of complex structural variants
While standard, short-read next generation sequencing (NGS) approaches have made DNA sequencing more accessible and are suitable for single nucleotide variant (SNV) detection, challenges still remain for complex structural variant (SV) reconstruction. Spanning hundreds and thousands of kilobases (Kb) to entire chromosomes, SVs come in many different flavors—from translocations, duplications, inversions, to more extreme versions, such as aneuploidy (loss or gain of an entire chromosome) and chromothripsis, (the shattering and random reconstruction of a chromosome) that are commonly associated with cancer.
Speaking at the 10x Bay Area User Group Meeting, Dr. Noah Spies, Stanford University, discussed using Linked-Read technology to overcome key challenges related to detecting complex structural variants with standard short reads in his presentation, "Genome-wide reconstruction of complex structural variants". Read more about the researchers' work in their Nature Methods publication.
The relatively large starting size of the input DNA molecules (>50Kb) and the 10x barcoding scheme used for Linked-Read library construction enable researchers to take advantage of the accuracy and efficiency of short-read sequencing while preserving long-range information. Spies noted that retaining long-range information was particularly useful when trying to relate complex SV events over long distances (e.g., SVs with multiple breakpoints) and for overcoming genome repetitiveness by linking ambiguous reads to flanking regions with unique sequence. Because the same barcode is added to all reads originating from the same long DNA molecule, most reads can be grouped or clustered into long molecules inferred from Linked-Reads, called Read Clouds.
Read Clouds can be used for SV detection by looking at and comparing each position in the genome where barcodes overlap to build a similarity matrix that looks for distant genomic regions that share high barcode similarity. Spies pointed out that one of the key advantages of Linked-Reads is the ability to identify SVs even if no short reads map to the breakpoint regions (e.g. high GC content region), as barcodes that map farther away from the breakpoint can still be used to detect a SV. This methodology can be applied to relatively straightforward SVs like single translocation events, as well as more complex SVs with multiple breakpoints, spanning multiple chromosomes.
In addition to SV detection, Linked-Reads were used to reconstruct the exact sequence of some of the SVs. For example, after identifying the 60 barcodes related to an SV event, Spies used the reads associated with those barcodes to assemble contigs that covered upstream, downstream and through the breakpoint of a Chromosome 5/7 translocation.
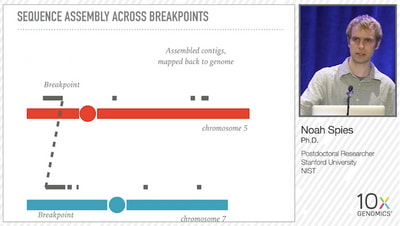
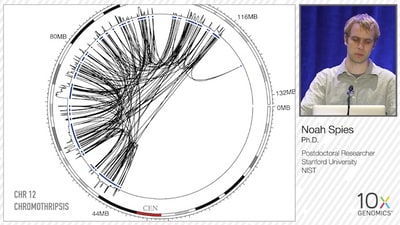
To test the Genome-wide Reconstruction of Complex Structural Variants (GROC-SVs) methodology, Spies et. al. examined 7 spatial samplings from a large (>20cm) liposarcoma tumor, as well as matched normal samples. The starting input molecule size is very important for optimizing SV detection, and Spies noted that his team performed a pulse-field gel size selection for fragments >50Kb when working with DNA from solid tumors, since maintaining DNA integrity during homogenization is difficult. However, when working with cultured cell lines, no size selection step was necessary. They identified >400 SVs in the tumor samples, including a typical case of chromothripsis on chromosome 12.
Overall, Spies and team were able to use Read Clouds to look at long-distance connectivity information from Linked-Reads and develop a statistical approach for SV detection. The 10x Linked-Read barcodes facilitated local breakpoint assembly and reconstruction of the order and sequence of complex SVs. When compared to standard short-read whole genome sequencing data, the Linked-Read data showed a reduced number of false positives and increased sensitivity when validated against long-insert mate pair data. Spies finished up by noting that 10x Read Cloud-based SV reconstruction shows significant progress towards whole genome SV measurement in cancer.
Watch the full presentation for more details and data examples.
Read the Nature Methods pub Genome-wide reconstruction of complex structural variants using read clouds
Additional Resources
- GROC-SVs on GitHub
- Chromium™ Structural Variant Analysis with Linked-Reads Application Note
- Learn more about Linked-Reads
- Sample Prep Demonstrated Protocols for sample QC and size selection
- See the Chromium™ Genome Solution
Check out more Linked-Read blog posts
