The Flex v1 and v2 workflows measure RNA levels in fixed samples using probes targeting the whole transcriptome. After whole transcriptome probe panels are added to the sample, each probe pair hybridizes to its target gene and is then ligated. Libraries are generated from the barcoded probes and sequenced.
The final sequencing library structure is similar to Gene Expression solutions for fresh frozen tissue, but the synthetic probe DNA is sequenced rather than the cDNA of a captured transcript. The final library structures for the Gene Expression library and Antibody Capture library are shown in the appropriate User Guides.
Key advantages of Flex include:
- Process formaldehyde fixed or formaldehyde fixed & paraffin embedded (FFPE) samples (single cells or nuclei)
- Increased sample throughput in a single GEM Well with multiplexing (up to 384-plex with Flex v2)
- High-sensitivity whole transcriptome amplicon (WTA) profiling with efficient sequencing
- Potential to retain multiplet data if each cell has a unique Probe Barcode or Antibody Multiplexing Barcode for Antibody Capture library (labeled "demultiplexible doublet" below). Here are four examples of GEMs with a 10x Genomics gel bead (dark blue) and zero, one or more cells (red or green):

Four examples of GEMs with 10x Genomics gel bead (dark blue) and zero, one, or more cells (red or green).
Here are example GEM-X Flex v2 workflows:
- Singleplex: one sample, one sample barcode, two libraries (CG000841)

- Multiplex: four samples, four sample barcodes, two libraries (CG000835)
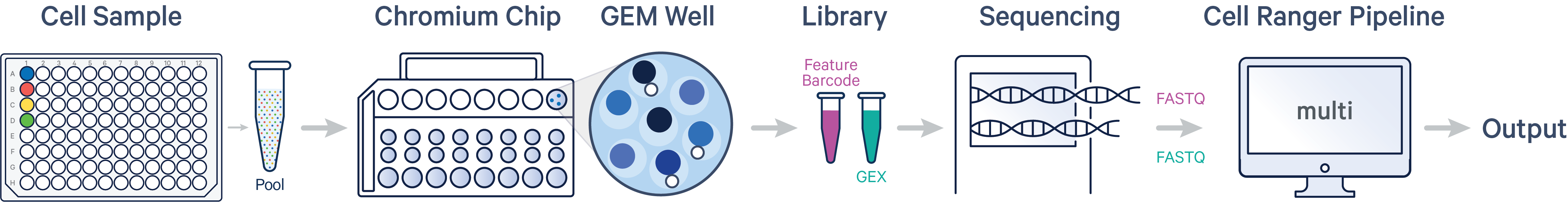
- Multiplex: two samples, two sample barcodes per sample, two libraries (CG000835)
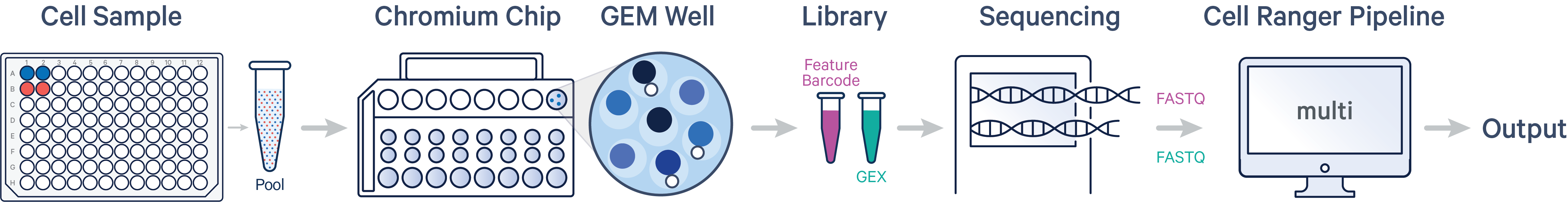
Here are example GEM-X Flex v1 workflows:
- One sample, one Probe Barcode, one library (CG000786)

- One sample, one Probe Barcode, two libraries (CG000788)
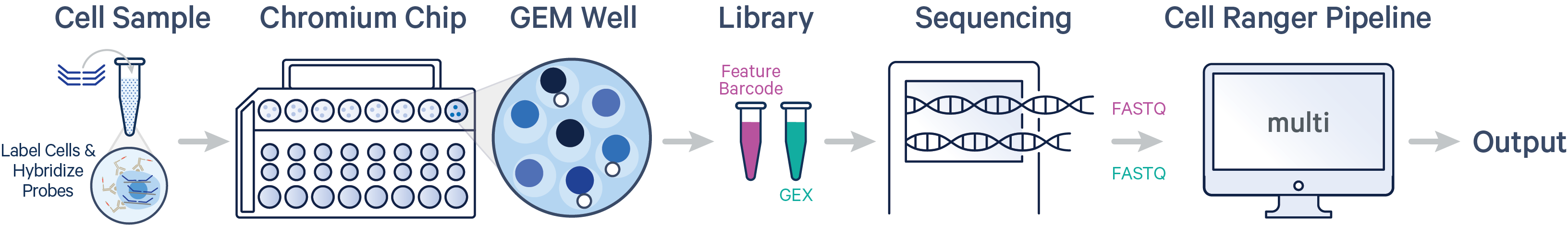
- Multiple samples, multiple Probe Barcodes, one library (CG000787)
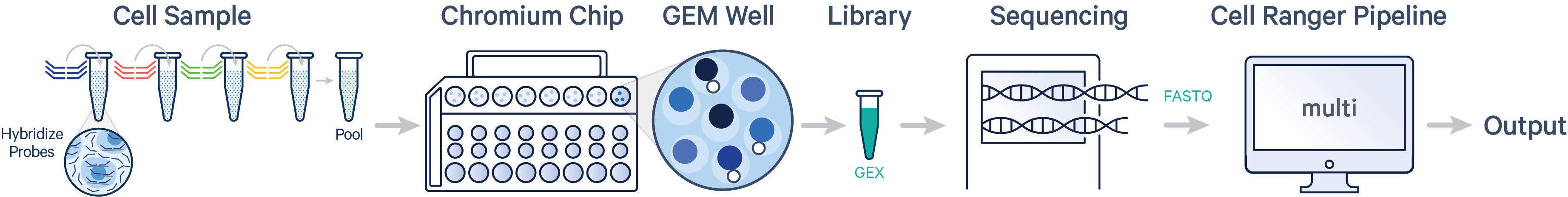
- Multiple samples, multiple Probe and Antibody Multiplexing Barcodes, two libraries (CG000789)

Cell Ranger v7.0 or later is required to analyze Flex v1 data and v10.0 or later is necessary for Flex v2 (see Supported Libraries table).
One or more samples are each uniquely tagged with a Probe Barcode (v1) or Sample Barcode (v2) prior to pooling in a single GEM Well, resulting in a Gene Expression (GEX) library for each GEM Well.
Flex Gene Expression workflows are compatible with:
- Cell surface protein Feature Barcode technology with TotalSeq™-B, TotalSeq™-C, or Proteintech Genomics (PTG)-derived antibodies.
- CRISPR Guide Capture Feature Barcode technology.
To analyze Flex libraries using the cellranger multi pipeline, follow these steps:
STEP 1: Gather your input files
Here is a list of all required inputs to run cellranger multi. The two main inputs are FASTQ files and the multi config CSV.
- Generate FASTQ files: If your sequencing core provides you with BCL files, you must first convert them to FASTQ format.
- Set up your multi config CSV. Learn about the Flex-specific sections and how to set it up:
STEP 2: Run the multi pipeline
Instructions for setting up the multi command and running the pipeline are provided here. Specifically, refer to the Inputs, arguments, and config section.
STEP 3: Review outputs
All the output files, including ones specific to Flex are described here to help you understand the results of your analysis.
Additional step: Algorithm details
For deeper insights, refer to details on the algorithm. Flex Gene Expression relies on the same underlying Cell Ranger analysis software as Universal 3’ Gene Expression solutions, but uses a short read aligner tailored to probe sequences. The probe aligner assigns probe and gene IDs to reads originating from ligation of correctly paired probe halves, distinguishing from potential artifacts and non-probe reads. For fixed samples, Cell Ranger counts oligo ligation events to build the feature-barcode matrix. As a consequence, if the probe hybridizes to a transcript with a variant, that variant will not be present in the sequencing data. Probes are designed to avoid known SNPs. For information on the probe sets, please visit the Probe Set Overview page.